Tesla’s factories are as much of a product as the cars that we drive or the Powerwalls that we use. “The machine that builds the machine” is a favorite Muskism that Tesla likes to drive home. Because without the rapid build-ups of these factories, Tesla would not be able to expand at the rate at which they do and make EVs as visible as possible. Here we have compiled recent Tesla production numbers by year for your reference as well as given an overview of each Tesla factory from a production and history standpoint.
2021 Tesla Production Numbers |
|||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model S/X |
0 |
2,340 |
TBA |
TBA |
2,340 |
| Model 3/Y |
180,338 |
204,081 |
TBA |
TBA |
384,419 |
|
180,338 |
206,421 |
TBA |
TBA |
TBA |
|
2021 Tesla Delivery Numbers |
|||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
| Model S/X |
2,020 |
1,890 |
TBA |
TBA |
3,910 |
| Model 3/Y |
180,338 |
199,360 |
TBA |
TBA |
379,698 |
|
184,800 |
TBA |
TBA |
TBA |
201,250 |
|
|
Actual Tesla Deliveries in Q1/Q2/Q3 2020 and Estimates for Q4 2020 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
USA |
Canada |
Europe |
China |
APAC |
Total |
||||
|
Q1 |
Model S/X |
Fremont |
7,240 |
632 |
2,596 |
1,192 |
570 |
12,230 |
|
|
Model 3 |
Fremont |
24,005 |
4,023 |
21,147 |
1,377 |
7,406 |
73,975 |
76,266 |
|
|
Shanghai |
16,017 |
||||||||
|
Model Y |
Fremont |
2,291 |
2,291 |
||||||
|
Shanghai |
|||||||||
|
Total |
33,536 |
4,655 |
23,743 |
18,586 |
7,976 |
88,496 |
|||
|
Q2 |
Model S/X |
Fremont |
7,214 |
345 |
2,002 |
928 |
125 |
10,614 |
|
|
Model 3 |
Fremont |
14,325 |
2,803 |
11,943 |
306 |
3,923 |
63,793 |
80,277 |
|
|
Shanghai |
30,493 |
||||||||
|
Model Y |
Fremont |
16,049 |
435 |
16,484 |
|||||
|
Shanghai |
|||||||||
|
Total |
37,588 |
3,583 |
13,945 |
31,727 |
4,048 |
90,891 |
|||
|
Q3 |
Model S/X |
Fremont |
8,048 |
405 |
3,226 |
2,486 |
1,110 |
15,275 |
|
|
Model 3 |
Fremont |
23,801 |
4,300 |
24,053 |
92 |
7,918 |
94,049 |
124,318 |
|
|
Shanghai |
33,885 |
||||||||
|
Model Y |
Fremont |
27,899 |
2,370 |
30,269 |
|||||
|
Shanghai |
|||||||||
|
Total |
59,748 |
7,075 |
27,279 |
36,463 |
9,028 |
139,593 |
|||
|
Q4 |
Model S/X |
Fremont |
12,824 |
414 |
3,374 |
2,710 |
877 |
20,199 |
|
|
Model 3 |
Fremont |
27,745 |
4,586 |
23,754 |
20 |
6,686 |
128,534 |
163,513 |
|
|
Shanghai |
33,885 |
||||||||
|
Model Y |
Fremont |
27,899 |
2,370 |
34,979 |
|||||
|
Shanghai |
0 |
||||||||
|
Total |
73,402 |
7,146 |
34,028 |
61,573 |
7,563 |
183,712 |
|||
|
2020 |
Model S/X |
Fremont |
35,326 |
1,796 |
11,198 |
7,316 |
2,682 |
58,318 |
|
|
Model 3 |
Fremont |
89,876 |
15,712 |
80,897 |
1,795 |
25,933 |
360,351 |
444,374 |
|
|
Shanghai |
0 |
0 |
6,900 |
139,238 |
0 |
||||
|
Model Y |
Fremont |
79,072 |
4,951 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
84,023 |
||
|
Shanghai |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
||||
|
Total |
204,274 |
22,459 |
98,995 |
148,349 |
28,615 |
502,692 |
|||
Table, figures, and estimates provided by @TroyTeslike
[/expand]
2020 Tesla Delivery Numbers |
|||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model S/X |
12,230 |
10,614 |
15,275 |
18,966 |
57,085 |
| Model 3 |
76,266 |
80,277 |
124,318 |
161,701 |
442,562 |
|
88,496 |
90,891 |
139,593 |
180,667 |
499,647 |
|
2019 Tesla Delivery Numbers |
|||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
| Model S/X |
12,091 |
17,722 |
17,483 |
19,475 |
66,771 |
| Model 3 |
50,928 |
77,634 |
79,703 |
92,620 |
305,885 |
|
63,019 |
95,356 |
97,186 |
112,095 |
372,626 |
|
2018 Tesla Delivery Numbers |
|||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
| Model S/X |
21,815 |
22,300 |
27,710 |
27,607 |
99,432 |
| Model 3 |
8,182 |
18,440 |
56,065 |
63,359 |
138,682 |
|
29,997 |
40,740 |
83,775 |
90,966 |
245,478 |
|
[/expand]
2020 Tesla Delivery Numbers |
|||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model S/X |
15,390 |
6,326 |
16,992 |
16,097 |
54,805 |
| Model 3 |
87,282 |
75,946 |
128,044 |
163,660 |
454,932 |
|
102,672 |
82,272 |
145,036 |
179,757 |
509,737 |
|
2019 Tesla Production Numbers |
|||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
| Model S/X |
14,163 |
14,517 |
16,318 |
17,933 |
62,931 |
| Model 3 |
62,975 |
72,531 |
79,837 |
86,958 |
302,301 |
|
77,138 |
87,048 |
96,155 |
104,891 |
365,232 |
|
2018 Tesla Production Numbers |
|||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
| Model S/X |
24,728 |
24,761 |
26,903 |
25,161 |
101,553 |
| Model 3 |
9,766 |
28,578 |
53,239 |
61,394 |
152,977 |
|
34,494 |
53,339 |
80,142 |
86,555 |
254,530 |
|
[/expand]
“How many Tesla factories are there?” is probably a question that is often asked, and we can see why. Even though it has not even been ten years since the release of the Model S, Tesla has expanded at such a rate that it doesn’t seem real. As soon as Tesla unveils a new model it tends to be packaged with a new factory in a brand new country that starts producing the car in about a year’s time.
Below you will find an overview of Tesla’s current and planned factories along with some estimated information regarding Tesla’s production capacities and what they produce.
Tesla’s Factory Locations |
||
|---|---|---|
Tesla Fremont Factoryest. 2010 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Location: Fremont, California, U.S. |
||
|
Current Capacity: ~7,900/wk |
|||
|
Maximum Capacity: ~600,000/yr |
|||
|
Model S |
Model X |
Model 3 |
Model Y |
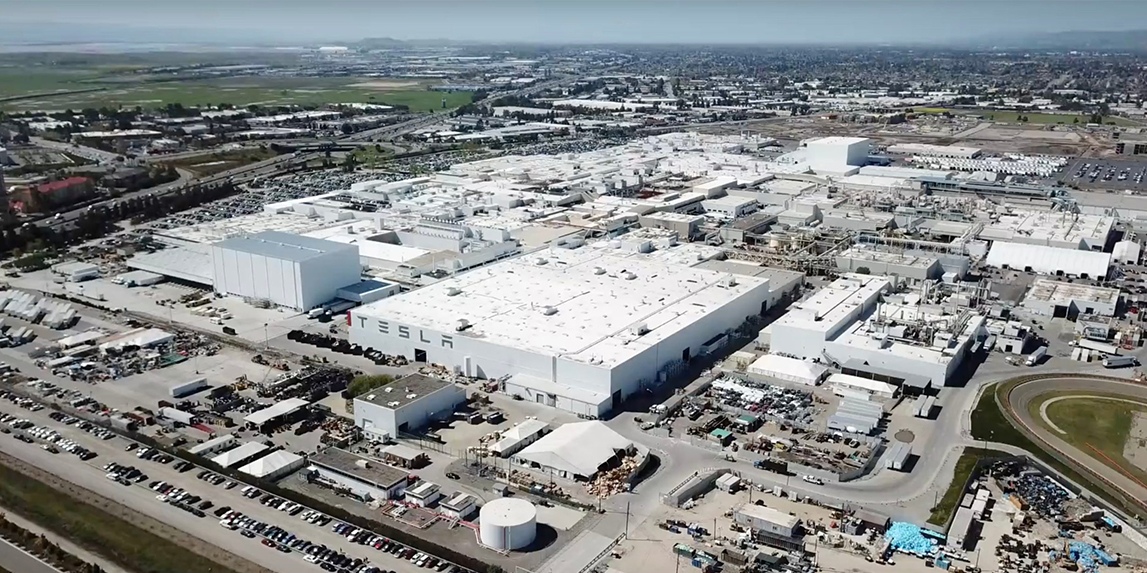

The companies movement into their current Tesla Fremont factory serves as a poetic metaphor of the changing times in the automotive world. What once was a factory used by goliaths like General Motors and Toyota, would now be the birthplace of an electric forerunner. Interestingly enough the Tesla Fremont factory that we all hold so dear was not the companies first choice. Initially, the electric startup wanted to build their own 157,000 sq. ft. production facility in Albuquerque, New Mexico and even got far as announcing the plan to the public in early 2017. However, things fell through and for the next few years, Tesla was trying to find another home for production.
Their eventual home would become a Tesla factory in Fremont, California used by New United Motor Manufacturing, Inc. (NUMMI), a joint-venture between General Motors and Toyota. The factory first came online in 1960 as GM Fremont before changing hands to the new joint venture in 1984. The plant produced various Toyota and GM cars and would hit a peak production rate of just over 428,000 cars. The joint venture would come to a close in 2009 due to the global recession and as such the NUMMI factory was going to be left without an owner. And so the factory was shut down in March 2010, but not for long.
Only a few months later Tesla and Toyota announced a partnership that would see Tesla help with producing and developing electric cars and their components, such as the second-generation Toyota RAV4 which uses a Tesla powertrain. As part of the deal, Tesla would purchase a large portion of the factory for only $42 million. The Tesla factory was initially dismissed partly due to the fact that it was too large for what they needed at 370-acre (16,000,000 sq. ft.),(remember their first planned facility was only 157,000 sq. ft.) but at a price that low and after years of searching, I’m sure it was hard to turn down. The purchase price did not include any of the equipment in the facility, so those pieces had to also be purchased by Tesla, but at a nice discount since they were second-hand.
Tesla would officially open up the factory in October 2010 and have their first Model S be delivered at a special event taking place at the Tesla Fremont Factory in June of 2012. While initially the Tesla production lines were done in a small portion of the available space (they were making 20,000 Model S in a factory that used to do over 400,000 cars), they incrementally expanded out whilst giving a face-lift to the interior of the factory.
Tesla did however eventually make full use of their original purchase and in 2016 were approved to further develop the factory to double its useable area to 10 million sq. ft.
Tesla Fremont Factory Delivery Numbers |
|||||
| 2020: |
72,479 |
60,398 |
105,708 |
117,969 |
356,554 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model S/X |
12,230 |
10,614 |
15,275 |
20,199 |
58,318 |
| Model 3 |
57,958 |
33,300 |
60,164 |
62,791 |
214,213 |
| Model Y |
2,291 |
16,484 |
30,269 |
34,979 |
84,023 |
The Tesla Fremont Factory continues to be the main hub when it comes to producing any of Tesla’s vehicles. Starting from the Model S, every new model of Tesla has been and continues to be produced at the Fremont Factory. The location continues to be the location for many Tesla events and reveals and serves as a spot of pilgrimage to any Tesla superfan. The company currently has plans for the Fremont factory to have a production rate of half a million cars, eclipsing the previous limit that the NUMMI factory was capable of outputting. Not bad for some discarded factory from the 60s.
Gigafactory 1est. 2016 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Location: Storey County, Nevada, U.S. |
||
|
Current Capacity: >39 GWh/yr |
|||
|
Maximum Capacity: Unbound |
|||
|
Components |
Batteries |
||
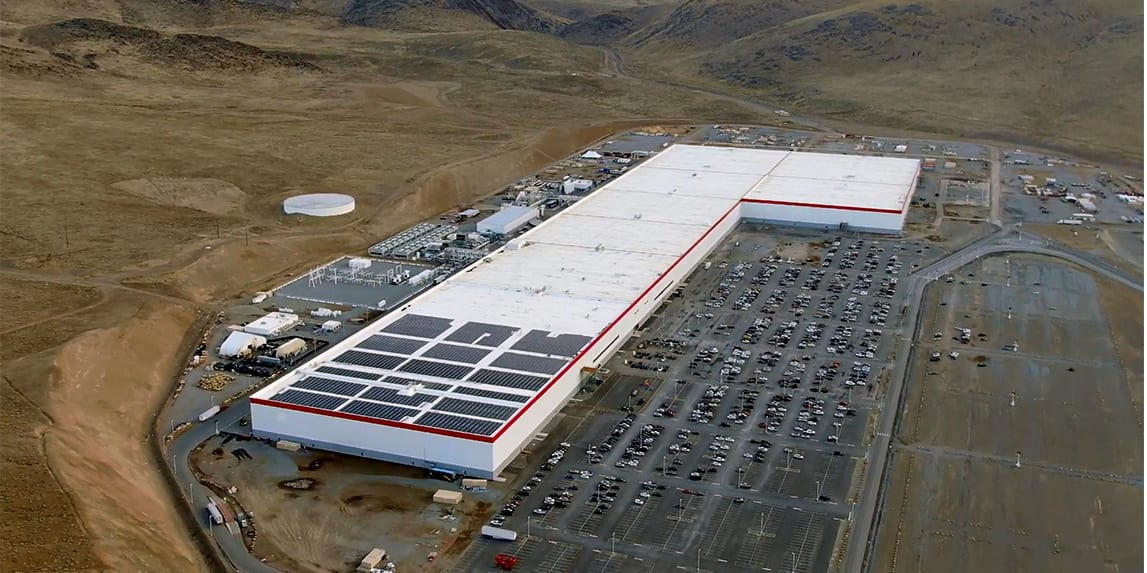

The OG Tesla Gigafactory, sometimes referred to as Giga Nevada, is the site of the production of Tesla’s batteries. After Tesla took possession of the Fremont Factory and started producing cars, they set their sights on establishing a stable supply of batteries for their new cars and upcoming Powerwall. The prospective locations were once again in the American Southwest with the states of Nevada, New Mexico, Arizona, and Texas. Once again, the chosen location did not seem to be the one that Tesla had initially thought they were going to use. Apparently, Northern Nevada was not high on Musk’s list of Gigafactory locations but after constant pestering by the head of the Tahoe-Reno Industrial Center and VP of airport economic development at Reno-Tahoe International Airport to come and visit the site, Musk and Tesla were convinced.
Just as with the Fremont Factory, the first Tesla Gigafactory would be born out of a partnership with a Japanese company. This time it would be Panasonic who would help Tesla with cell and battery pack production. However, Tesla would not get a steal of a price for the factory this time around as they would have to build it from scratch. Tesla’s Gigafactory 1 would end up costing about $5 billion. Initially, Panasonic was going to commit $1.6 billion to the project, but after seeing the early demand for the Model 3 the company raised $3.86 billion in corporate bonds, a majority of which would go to towards the factory.
Construction of the factory started in late 2014 and was “finished” in 2016, ahead of the Model 3 launch. I say “finished” because Giga Nevada has been in a weird state of limbo in regards to its construction status. Even though it has about 1.9 million sq. ft. of space, the factory is only about 30% complete with plenty of room for expansion. Given that Tesla is more than capable of producing multiple factories simultaneously, it seems odd that Gigafactory 1 has not seen an expansion.
Gigfactory 1 does not have any vehicles produced in its walls as all the production is dedicated to battery production for the cars and Powerwalls as well as electric motors. There have been rumors about maybe a model being produced there eventually, but that would probably require an expansion.
The original guidance for Gigafactory 1 saw the factory being able to produce 35 GWh at the cell level and 50 GWh at the pack level to support about 500,000 vehicles by 2020. The factory seemed to have reached a theoretical output of 35 GWh by 2019 and in August 2020 received a rare expansion that saw its output grow to 39 GWh, although it is hard to tell if Tesla is hitting the full capacity of the factory.
Once again, the Nevada Gigafactory was an important milestone for Tesla who was able to build its own factory and start producing car batteries in huge quantities that would prepare it to deliver its mass-market Model 3. While the scale might have been impressive, the batteries produced in Gigafactory 1 is only the tip of the iceberg in terms of planned production from Tesla. During Battery Day, Tesla announced its goal of outputting 3TWh (3000GWh) worth of batteries and we were introduced to the concept of Terrafactories. As you imagine, it’s like a Gigfactory, but making batteries in the TerrawattHour worth. No doubt that Tesla has learned a lot from its experiences in Gigafactory 1 that will help them in its goals of making a Terrafactory.
Gigafactory 2est. 2017 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Location: Buffalo, New York, U.S. |
||
|
Current Capacity: N/A |
|||
|
Maximum Capacity: N/A |
|||
|
Solar |
|||
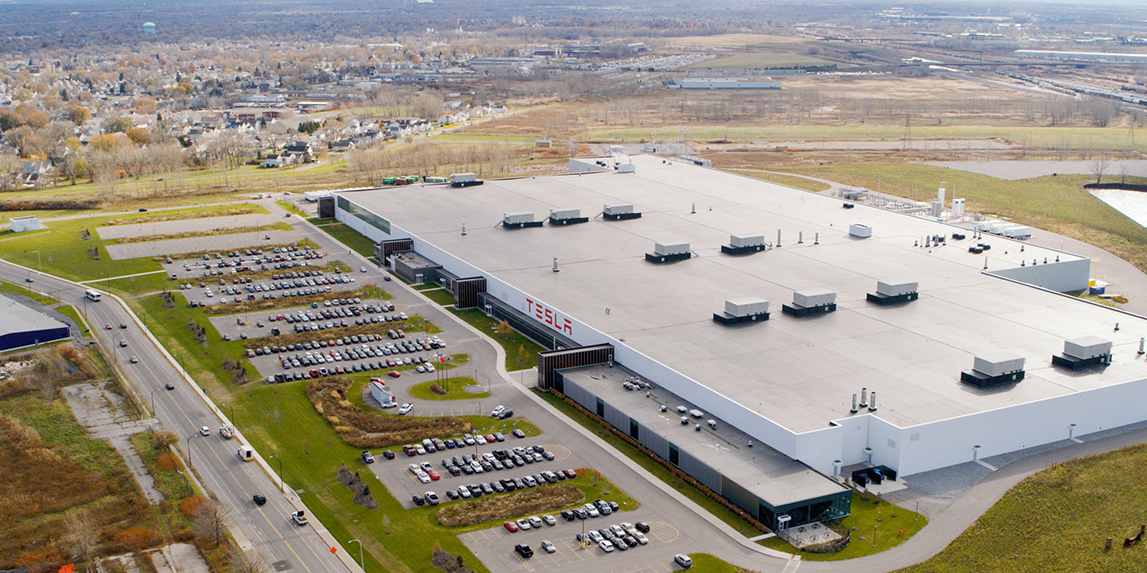

Gigafactory 2, also known as Giga New York, is probably the most removed from the typical factory that is in Tesla’s lineup but nonetheless served as an indicator for Tesla expanding outside of just automobiles.
Built on the former site of a steel mill in Buffalo, New York, Gigafactory 2 was not built from the ground up by Tesla. Instead, the construction of the factory was handled by the State of New York as they tried to use the site as a possible green energy incubation center. One of the two planned tenants of the building was solar panel producer Silevo. Prior to the start of construction of the facility in 2014, Silveo was acquired by SolarCity, which Elon Musk was the Chairman of until 2016. After the acquisition, the plans for the factory were greatly expanded to 1.2 million sq. ft. of space and an investment of up to $5 billion from SolarCity.
Construction of the factory would begin in September 2014 and would be fully up and running in August 2017. In the meantime, SolarCity would become a subsidiary of Tesla in 2016, giving Tesla control of the solar panel factory. Just as with Gigafactory 1, product development in Gigafactory 2 is done with Panasonic. However, in early 2020 it looked like the two would be parting ways as Tesla’s newest solar product, the Solar Roof, does not use Panasonic’s PV cells and instead uses cells from China. Panasonic however does still seem to work in the factory to help produce the battery cells that are used in the Powerwall and Powerpack.
Tesla factory Buffalo is certainly the least glamourous of Tesla’s factory lineup. It however does serve as a strong foundation if Tesla wants to expand its business outside of automobiles. Being the factory that produces all of Tesla’s home offerings like the Powerwall and new Solar Roof, it might serve a more important role sometime in the future. On top of all batteries and solar panels, the factory is also responsible for Tesla producing Superchargers, an invaluable part of Tesla’s success with EV adoption by providing enough charging points to not have to go out of your way to charge.
It seems like we will get more factories similar to Gigafactory 1 in the future to address EV battery demands, will we see future Gigafactory 2-like facilities in the future for solar panels?
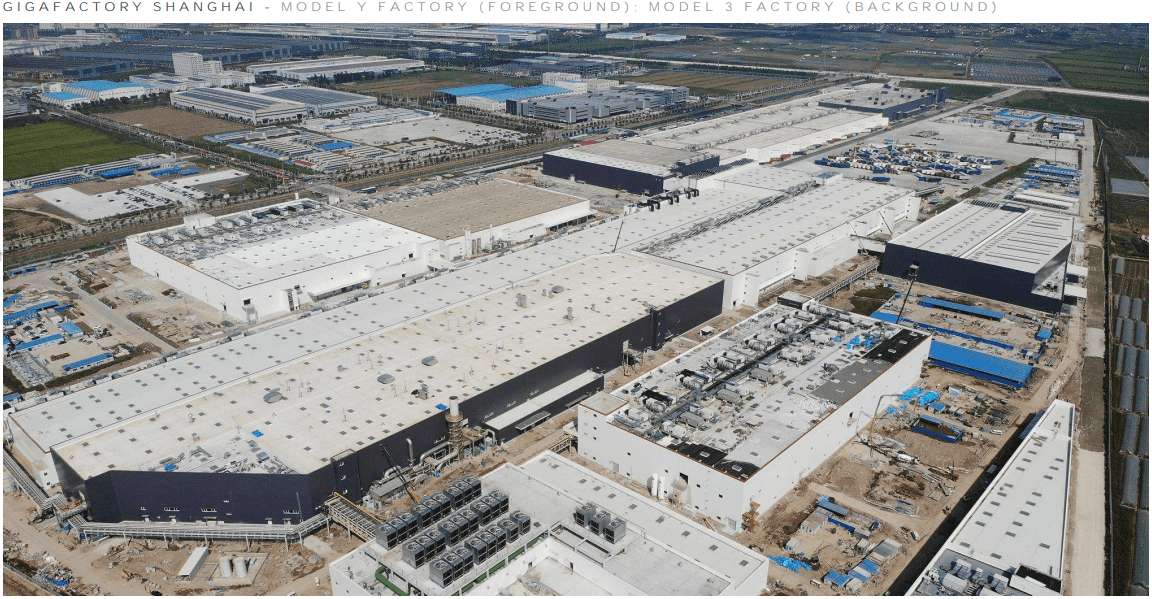
Giga Shanghaiest. 2019 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Location: Pudong, Shanghai, China |
||
|
Current Capacity: ~6,850/wk |
|||
|
Maximum Capacity: ~500,000/yr |
|||
|
Model 3 |
Model Y |
||
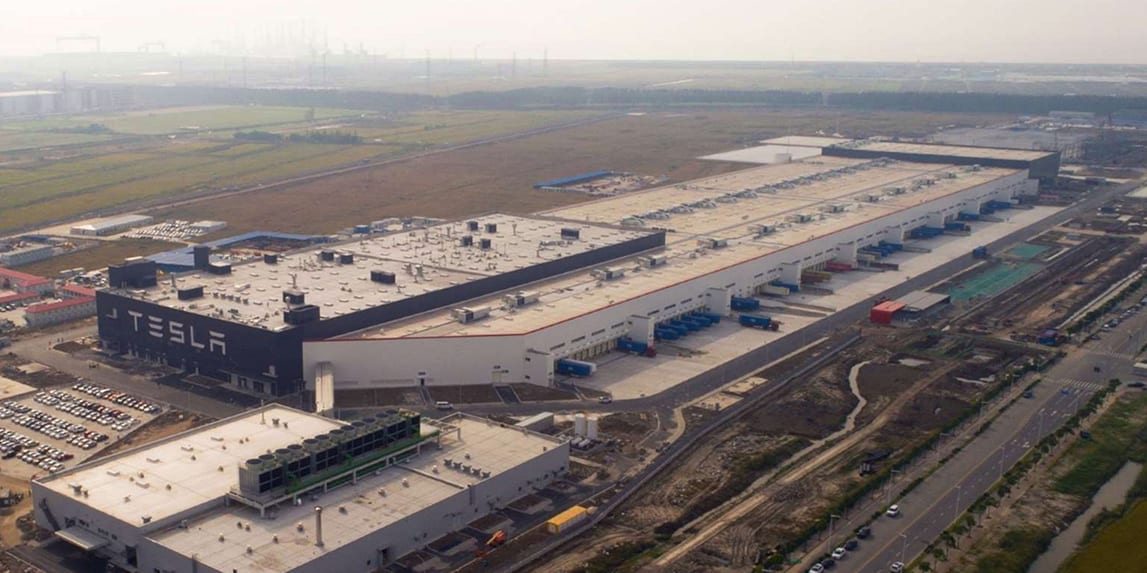

Giga Shanghai would be another important step as it would be the first time they went international, building a Tesla factory in China. With the demand for the Model 3 reaching huge numbers, the Tesla factory in Fremont was having trouble keeping up with Tesla production numbers and a need for another factory to produce cars became a necessity. Given that international demand for the Model 3 was also high, it made sense to create a Tesla factory outside of US borders to cut down on transportation and possible taxation of imports. With the political climate between the US and China always being tense, new tariffs on products tend to get thrown around without hesitation. One tariff causes a huge increase in the price of the Model S/X in China. With the Model 3 intended to be a mass-market car, severe tariffs increasing its price would basically make it dead on arrival in the lucrative Chinese market.
So in late 2018, Tesla purchases land in Shanghai, China which would be the home of Tesla Gigafactory 3 and would produce both the Model 3 and future Model Y. The factory would not only be an achievement due to it being an international expansion but also due to the rate at which the factory was built. Overcoming and learning from initial Tesla production problems made this process a bit quicker. With construction set to begin at the very end of 2018, the first Model 3 was off the production line in December 2019, less than a year later. To be clear, however, the factory was not fully done and not all the Tesla production lines were in place, but as soon as they had to space for one or two production lines, Tesla started using them while finishing construction of the Tesla factory.
Initially, these Model 3’s were still made of parts shipped from the US and were in China for their final assembly. However, as 2020 went on, the reliance on parts from the US dropped and we started to get Made in China (MIC) Model 3s. Not only did this allow Tesla to lower the price of the Model 3 and be more competitive, but it also allowed another avenue for export to the European countries which still did not have a factory of their own.
The Model 3 portion of the factory was finished in 2020 and was building up its Tesla production capacity as the year went on while the Model Y portion of the factory continued to be built. Starting in 2021 the Model Y portion of the factory will be operational and will start delivering MIC Model Ys. The initial goal for the factory has a Tesla production capacity of about 500,000 cars a year. According to a recent study, it looks like the factory was outputting a Tesla production rate of 8,000 cars a week (416,000 a year) with room to grow. So it looks like the facility is on track to meet its important production goals.
According to a study by Industrial Securities in China, Giga Shanghai has reached a production capacity of 8k units/week (5k 3s, 3k Ys) & is estimated to make 523k units for 2021 (278k 3s, 245k Ys), including 100k units for export. TBC. pic.twitter.com/VZiT1C6v4M
— Ray4Tesla⚡️🚘☀️🔋 (@ray4tesla) January 5, 2021
Tesla Gigafactory Shanghai Delivery Numbers |
|||||
| 2020: |
16,017 |
30,493 |
33,885 |
65,743 |
146,138 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 3 |
16,017 |
30,493 |
33,885 |
65,743 |
146,138 |
With a possible Tesla production capacity that overshadows how many cars Tesla made in 2020 across all factories, Tesla Shanghai is looking to overtake the Tesla factory in Fremont in terms of how many cars it can produce. As Asian continues continue to embrace electric cars, the Chinese Gigafactory will prove to be an invaluable piece in Tesla’s dominance.
Alongside the start of production at the Shanghai factory, Tesla also announced that they would open a Chinese design studio that would design a new model for Tesla that would be sold internationally. Many have speculated that this vehicle will be Tesla’s $25,000 passenger car, but no further information has been given by Tesla themselves.
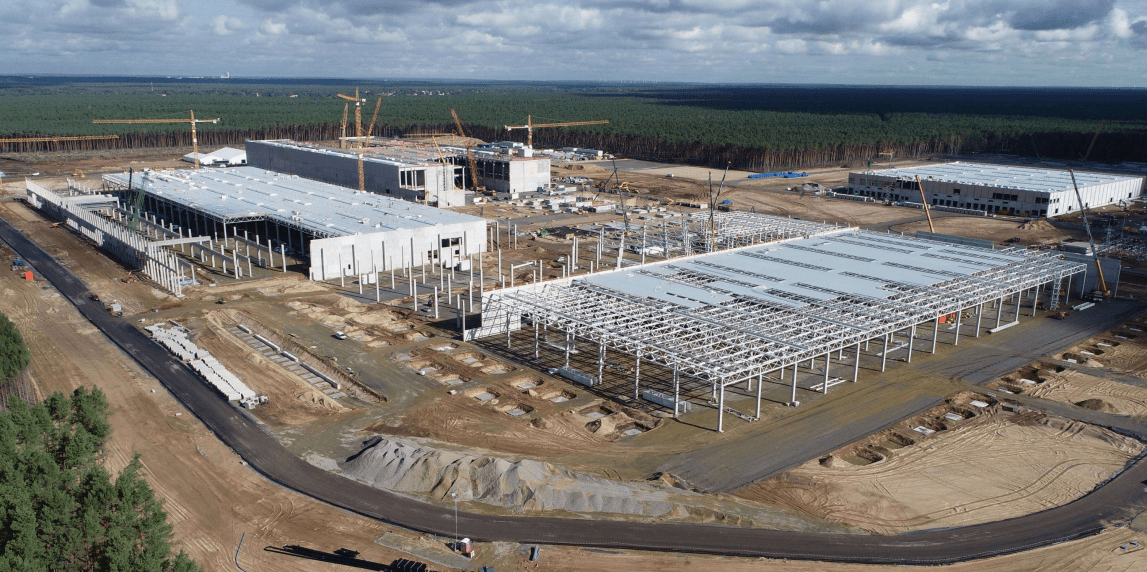
Gigafactory Berlinest. 2021 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Location: Grünheide, Brandenburg, Germany |
||
|
Current Capacity: N/A |
|||
|
Maximum Capacity: ~500,000/yr |
|||
|
Model 3 |
Model Y |
||
With North America and Asia covered, it was time for Tesla to turn its attention to Europe. Tesla’s jump to Europe looked to be in the works even prior to the completion of Gigafactory 1, but it would be some years before Tesla would move forward with the plan for a Tesla factory in Europe.
With Gigafactory 3 announced and Tesla looking to rapidly expand, discussion and rumors of a European Gigafactory heated up in mid-2018. Over the years, from 2015 to its official announcement in 2019, over ten European countries reportedly were putting bids to have their nation be the home of Tesla’s newest Gigafactory. Of all the countries, Germany was crowned the winner when Elon Musk made the announcement in November 2019 at the Golden Steering Wheel award show. The proposed location would be just 20 miles away from Berlin and would produce both the Model Y and Model 3 at a production rate of 500,000 cars a year.
The construction of Tesla’s Germany factory, or more specific Giga Berlin, started in early 2020 and is expected to begin operations in July 2021. It is still unclear as to when the factory will become 100% finished. Construction has met several small setbacks over the year that mostly had to do with environmental conservation and changes to the foundation, but it seems like the factory will be finished in time.
Unlike the Tesla factory in China, Gigafactory 4 will produce the Model Y before it produces the Model 3. Additionally, the Model Y produced in Europe will be considerably different from the one that is made in Tesla Fremont and Shanghai. During Tesla’s Battery Day, the company showed off its plans for a new 4680 battery cell as well as a structural battery pack that takes inspiration from gas tank wings found on planes. Along with those advancements, the European Model Y will also be the first to use Tesla’s front and rear single casting pieces, significantly reducing the parts in the car. On top of all that it will also use Tesla’s “most advanced” paint shop that will be found in Giga Berlin.
Berlin will use 4680 cell with structural battery pack & front & rear single piece castings. Also, a new paint system.
Lot of new technology will happen in Berlin, which means significant production risk. Fremont & Shanghai will transition in ~2 years when new tech is proven.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) October 7, 2020
It will take a while before some of these advancements make their way over to other Tesla Gigafactories, so look for the German Tesla factory to be the testing grounds for Tesla’s future production methods. As with Gigafactory 3, Tesla will also open a design studio alongside Gigafactory 4.
Giga Texasest. 2021 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Location: Austin, Texas, U.S. |
||
|
Current Capacity: N/A |
|||
|
Maximum Capacity: Unknown |
|||
|
Model Y |
Cybertruck |
||
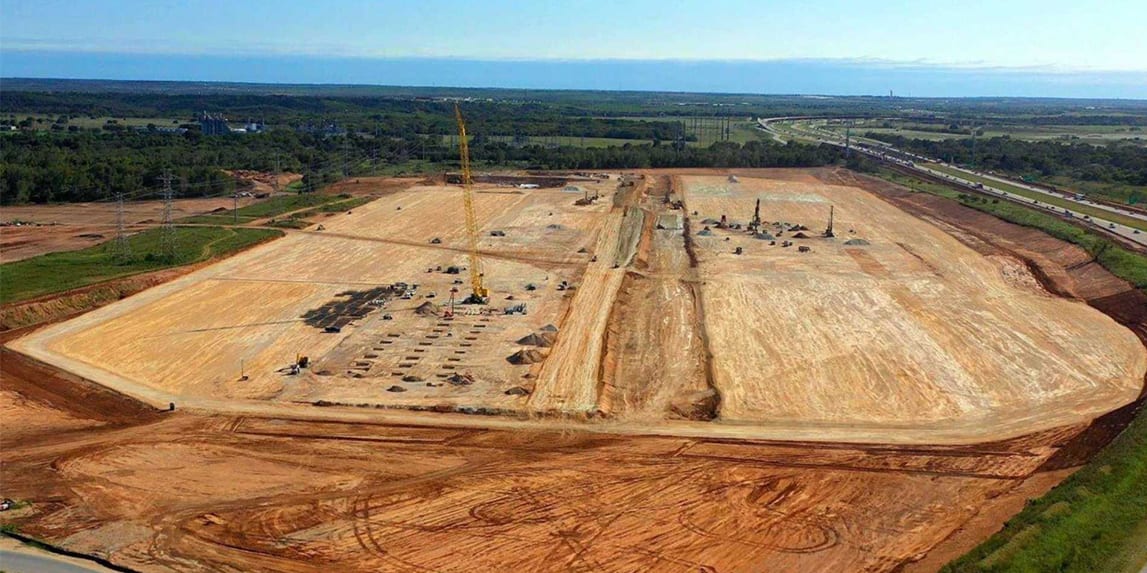

In late 2019 Tesla revealed the Cybertruck to the world. Many people hated it, but a lot of people also loved it. Two days after the reveal Musk tweeted that there were 200,000 orders and fan estimates have put todays reservation number at over 700,000 orders. All it cost was a $100 refundable deposit, so not all those reservations will convert to sales, but once again Tesla has a large backlog of vehicles to get through.
If you’ve been paying attention then you can guess that this would be the catalyst for yet another Tesla factory. With Asia and Europe now accounted for, Tesla could choose a location in North America again, this time closer to the East Coast so that it could have a more central location when compared to Tesla Fremont. With the Tesla truck production date ready start in late 2020, Tesla had to act quickly to start building a new factory.
After bids from multiple mid-western states, it appeared to have come down to either Tulsa, Oklahoma and Austin, Texas as the finalists. Tulsa offered both a statue of Elon Musk as well as a Big F—ing Field, but it still lost out to Austin when decision time came in mid-2020. Musk did however make a comment that he would like to eventually have something built in Tulsa.
Tesla Gigafactory 5 would start construction in July 2020 alongside both Gigafactory 3 and Gigafactory 4, showing off the multitasking and expansion efforts of Tesla. Giga Texas will not only be the site of Cybertruck production, but it will also produce the Tesla Model 3 and Model Y, because you cannot get enough of the Model 3/Y. Rumors have also been circulating that the Semi will also be produced in Tesla Terrafactory Texas, but I have not seen an announcement from Tesla stating as such. As with Giga Shanghai and Giga Berlin, expect a production capacity of 500,000 cars a year with room to expand.
If Tesla is set to meet their Cybertruck delivery date goal, then expect Giga Texas to start being operational at the end of 2021.
Tilburg Assembly Point
The Tilburg Assembly Point in the Netherlands has served as Tesla’s European distribution center since the company started production of the Model S in 2012. The relatively small (at least compared to a Tesla Gigafactory) facility does not do any of its own manufacturing and instead acts as a final assembly point for the Model S/X. The facility has grown in space over its history to accommodate the increase in Model S/X production since its inception.
We don’t imagine that Tesla will close down the facility after Giga Berlin is complete as it will only produce the Model 3/Y while Tilburg handles the American made Model S/X.
China Supercharger Factory
With Gigafactory 3 nearing completion at the end of 2020, Tesla was looking primed to make a max effort push in the Chinese market. To help support the planned influx of MIC Teslas on the road, Tesla announced that it would invest $6.4 million to build a factory near its Shanghai factory to produce Superchargers for China.
Some of the largest Supercharger stations (and the largest) are found within China, so clearly Tesla has put a huge emphasis on installing Superchargers in China. The factory is expected to be complete in the first quarter of 2021 and will be able to produce 10,000 stalls a year.
While some might think it’s foolish to speculate on yet another Tesla Gigafactory in the midst of the company just finishing one and currently in the process of building two others, you can see that Tesla doesn’t exactly like to have downtime. So here are some possible Tesla factory locations to look forward to. As always these are “rumored” and most of the evidence hinges on passing Twitter comments from Musk or secondary sources.
Giga Japan / Giga South Korea
The Asian continent is a large one, and so it wouldn’t be too surprising if Tesla were to plan another factory to help support future demand in Asian countries. When asked via Twitter, Musk responded that there will be a factory outside of China once Giga Berlin and Giga Texas are complete.
Yeah, but first we need to finish Giga Berlin and a second US Giga to serve eastern half of North America
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) July 5, 2020
The logical options outside of China would point to either a factory in Japan or South Korea. Both countries have strong automotive industries and both are close to battery suppliers to provide for Tesla (Panasonic in Japan and LG Chem in South Korea). There are certainly many considerations in location, Tesla has a long history with Panasonic, but would have to export all their cars by ship due to being on an island nation, for instance. Regardless, if we have to wait for the completion of both the Texas and Berlin factories, then it will be a while before we get more Tesla factory news.
Giga India
Tesla for a long time has been on the outside looking in when it comes to India. The company had continued to delay its plans to enter the emerging market. In late 2020, Musk replied to a tweet asking about Tesla’s Indian entry to which the CEO replied “next year for sure”
Next year for sure
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) October 2, 2020
And it seems that that tweet was more than talk as in early 2021 we received word that Tesla had incorporated an Indian subsidiary that looks to set up various facilities, including a possible factory. Given India’s bursting population we imagine that it represents an important market for Tesla and has a good chance to be the location for a new Gigafactory.
Tesla factory locations now reside across the globe with many more set to come.